- Conditions Treated
Overview
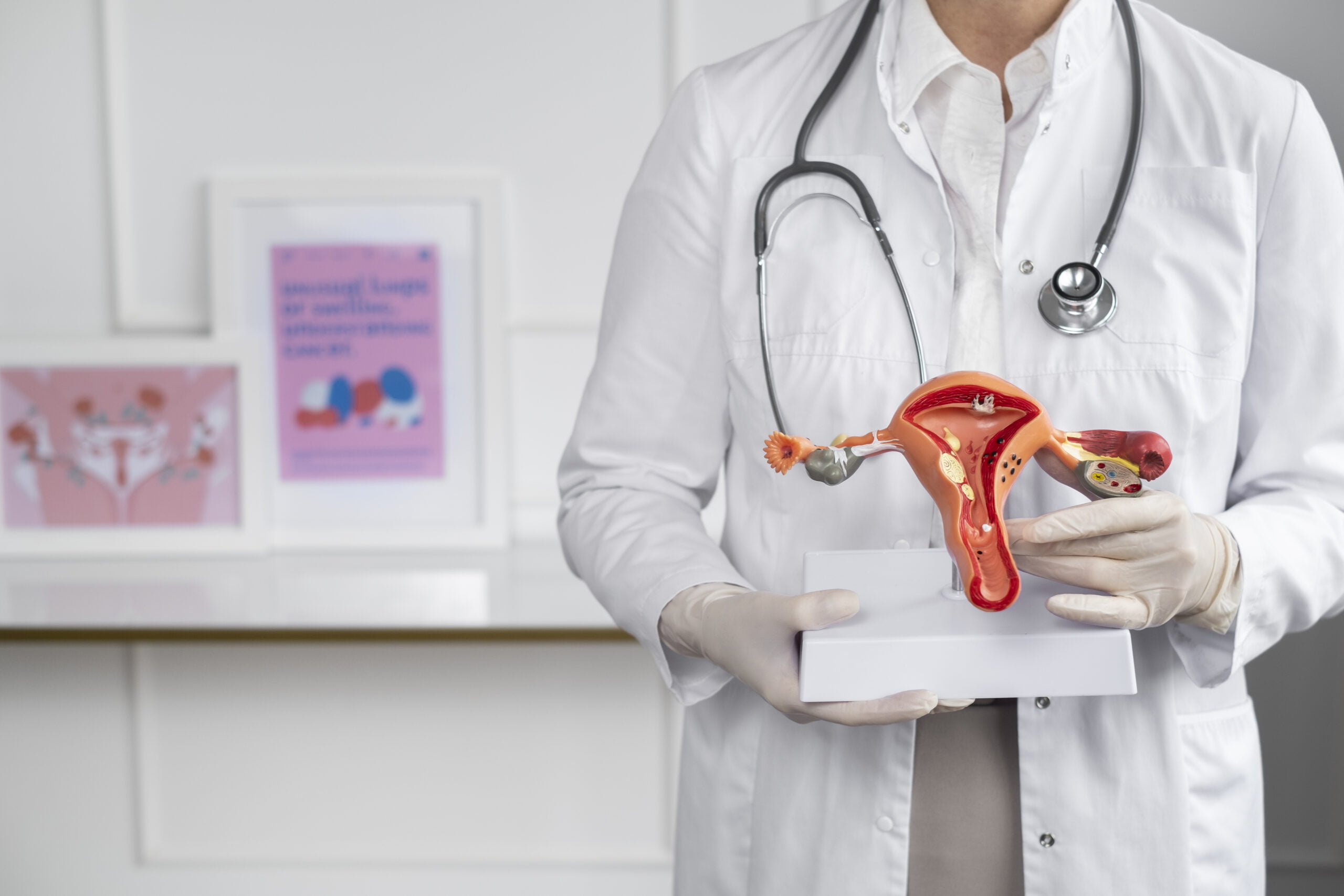
Endometriosis is a chronic condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus, or endometrium, begins to grow in places outside the uterus. This can include areas such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the outer surface of the uterus, and the tissues lining the pelvis.
This ectopic tissue responds to hormonal changes just like the endometrium, thickening, breaking down, and bleeding with each menstrual cycle. However, because it has no way to exit the body, it becomes trapped, leading to various problems.
Symptoms
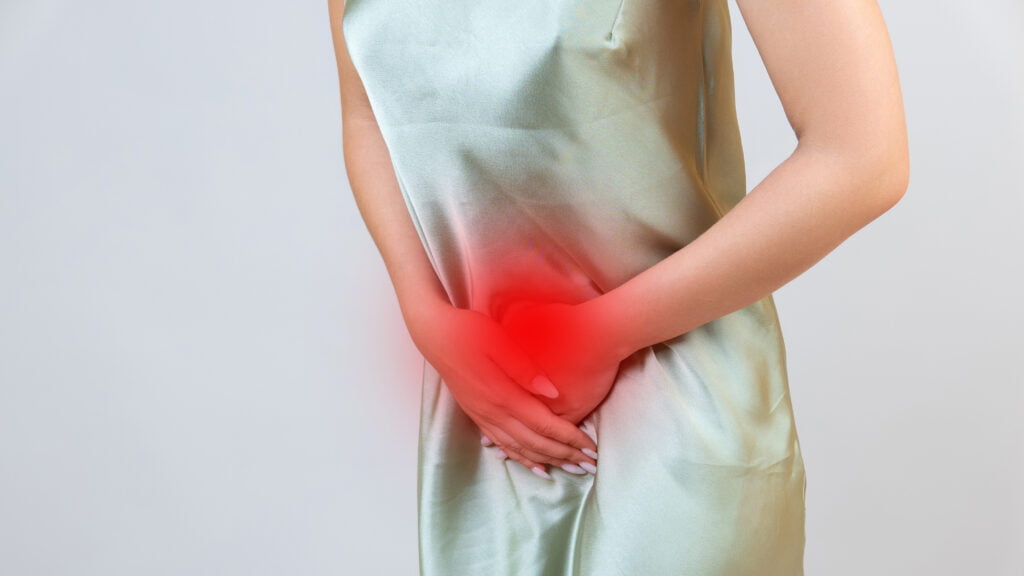
Pelvic Pain and Cramping: One of the most common symptoms is pain, especially in the pelvis and lower abdomen. This pain can be more intense during menstrual periods but might also be chronic.
Pain During or After Sexual Intercourse: Dyspareunia, or painful sex, is a common symptom of endometriosis, and can occur during or after the act.
Infertility: Endometriosis can lead to difficulties becoming pregnant. Some women discover they have endometriosis only when they seek treatment for infertility.
Treatment Approach
- Pain Medication: NSAIDs are often used to manage pain and discomfort from endometriosis.
- Hormonal Therapy: This treatment, which includes birth control pills, progestin IUDs, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists and antagonists, aims to regulate hormones that stimulate endometrial tissue growth.
- Surgery: Depending on symptoms and fertility goals, surgery can involve removing endometrial growths, or in more severe cases, a hysterectomy or oophorectomy.